Table of Contents
A decade of targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer
Published on: 28th September, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317653904
Chemotherapy is one of the main treatment options for cancer. However, chemotherapeutic agents usually suffer from poor pharmaceutical properties that restrict their use. Targeted therapy drugs have been developed to specifically target changes in cancer cells that help these cells to grow. Such drugs often work when standard chemotherapeutic drugs do not, they often have less severe side effects and they are most often used for advanced cancers. The objective of this article is to give an overview about the 16 FDA-approved targeted therapy drugs to treat non-small cell lung cancer.
Fluticasone furoate/Vilanterol 92/22 μg once-a-day vs Beclomethasone dipropionate/Formoterol 100/6 μg b.i.d. in asthma patients: a 12-week pilot study
Published on: 27th September, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317597138
Two of the most recent LABA/ICS combinations for treatment of persistent asthma are Fluticasone furoate/Vilanterol 92/22 µg (Ellipta) and Beclomethasone dipropionate/Formoterol 100/6 µg (Nexthaler).
Objective: To compare once-daily Fluticasone/ Vilanterol combination with twice daily Beclomethasone/ Formoterol association in moderate asthma, in terms of quality of life and lung function.
Methods: Fourty patients with moderate asthma treated with Beclomethasone/Formoterol 100/6 µg or Fluticasone/Vilanterol 92/22 µg. We revalued patients in terms of lung function and Asthma Control Test, at 4, 8 and 12 weeks to assess any differences between the two groups. After 4 weeks, thirty-one of the fourty patients were evaluated in terms of respiratory function at predetermined time intervals.
Result: In patients treated with beclomethasone/formoterol FEV1 presented a mean value of 78% at the third visit and of 79.1% during the final check, compared with 74.5% and to 75.8% in patients in treatment with fluticasone/vilanterol (p 0.01). Mean values of IC and MMEF25-75% were higher in patients treated with beclomethasone/formoterol compared with fluticasone/vilanterol. For the dyspnea it was a difference at the third observation. For the nocturnal symptoms and the use of rescue drug there was a significant difference, except at the beginning. For the perception of control by patients, there was a difference in the two groups at the beginning, after 4 and 8 weeks. Total ACT score showed a significant difference after 4, 8 and 12 weeks. In the group treated with beclomethasone/formoterol FEV1 value was significantly higher at a distance of four hours after drug administration (p 0.04) and after the second dose (p 0.02) compared with the group treated with fluticasone/vilanterol.
Discussion: Patients in treatment with beclomethasone/formoterol showed improved asthma control and nocturnal symptoms and more stable respiratory function compared with patients receiving fluticasone/vilanterol.
Successful Therapy with intravenous gamma globulin in two children with postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans
Published on: 23rd June, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317654734
Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO) is an infrequent clinical syndrome characterized by the chronic obstruction of small airways due to fibrosis [1]. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) could be used for treatment while underlying immune mechanisms in the pathogenesis of BO exist [2]. Here, we present two children with BO due to adenovirus infection whose complaints resolved after IVIG replacement.
Acute and chronic changes in massive Barium Sulfate aspiration in an infant who subsequently was diagnosed with severe Gastro-esophageal Reflux
Published on: 19th June, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317654649
The barium is often used in radiocontrast examinations of the digestive system because of mucosal absorption is limited. Massive barium aspiration is a rare complication, especially when there is no anatomic or neurological deficit. The depending on barium concentration can cause various lung effects. When the literature is reviewed, barium aspiration may be asymptomatic or lethal in massive amounts. Rarely, large amounts of barium sulphate are aspirated into the lung, there is no literature study how often this is happening.
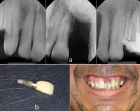
We present a case of massive barium aspiration in this subject. The case is related to a patient’s diagnostic esophagography who complaints swallowing problems. The massive barium aspiration couldn’t notice because of the absence of acute symptoms and surgical operation of gastrointestinal tract which the patient had undergone previously. When the patient applied our Pediatric Chest Diseases Polyclinic after three months, as a result of the examinations and deep research it was understood that the case was about massive barium aspiration. The patient was directed to our center because there was a radiological appearance of bone density signs on chest X-ray. Such a complaint was not reported by the family neighter in his biography, nor was written in the epicrisis. We will share acute and chronic changes in the lungs, diagnosis and treatment approaches of this case. The infant who has ileostomy was previously operated because of necrotizing enterocolitis. And also still has severe gastro-esophageal reflux and under conservative and medical treatment, a possible fundoplication surgery is planning.
Avoiding confusion in high flow oxygen therapy concepts
Published on: 31st May, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317646410
Oxygen therapy is the main supportive treatment in hypoxemic respiratory failure and has traditionally been delivered using low and high flow devices. However, the maximal flow rates that these devices can deliver are limited because of the insufficient heat and humidity provided to the gas administered. Low flow devices such as the nasal cannula, conventional face mask and reservoir bag deliver a flow rate of up to 15 L/min by administering more variable oxygen fractions (FiO2), depending on the patient’s respiratory pattern, peak inspiratory flow and characteristics of the devices. Conventional high flow devices, such as venturi type masks, utilize a constant flow of oxygen through precisely sized ports, entraining the ambient air, using the Bernoulli principle, providing a more constant inspired oxygen fraction. However, they are less tolerated than nasal cannulas because they are less comfortable and the insufficient humidification and heating of the gas delivered [1].
In the last two decades, new devices have been developed to administer high humidified and heated flow through a nasal cannula (HFNC) that also allows the delivery of oxygen with a known FiO2 up to 100%. In the literature, this technique has also been called mini CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure), transnasal insufflation, high nasal flow ventilation, high flow oxygen therapy, and high flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy [2].
It is considered that high flow nasal cannula has certain benefits compared to those of oxygen therapy previously detailed. HFNC manages a flow of more than 30 L/min, which is able to surpass the peak inspiratory flow of the patient, being able to reach values between 60-80 L/min depending on the flow used. The gas source, which may be delivered by an air/oxygen blender, fans, or a flow generating turbine, is connected by an active humidifier to a nasal cannula and the FiO2 can be adjusted independently of the flow.
From a clinical point of view, there is some confusion between venturi and high flow nasal cannula devices. In the literature, both have been considered as high flow oxygen therapy devices. In our opinion this is not appropriate because the high nasal cannula flow is much more than a simple system for administering oxygen therapy [3]. Venturi-type masks provide the patient with a gas mixture with a controlled FiO2, but do not exert additional benefits on the ventilator mechanics of the patient. Nevertheless, HFNC allows the delivery of a high flow, which can also add oxygen therapy, providing a series of physiological effects that imply an active treatment to respiratory failure.
Effects related to HFNC include the following:
1. Delivery of higher and more stable FiO2 values, because the flow delivered is greater than the patient’s inspiratory demand.
2. The anatomical dead space decreases by washing the nasopharynx, consequently increases alveolar ventilation. This improves the thoracoabdominal synchrony.
3. Respiratory work decreases because it acts as a mechanical stent in the airway and markedly attenuates inspiratory resistance.
4. The gas administered is warmed and humidified, improving mucociliar clearance, reducing the risk of atelectasis, improving ventilation perfusion and oxygenation ratio.
5. There is a CPAP-like effect. The dynamic positive espiratory airway pressure generated by HFNC reaches a value between 6-8cmH2o depending on the flow and the size of the cannula. This positive pressure distends the lungs and ensures their recruitment.
6. Pulmonary end-expiratory volume is higher with HFCN than with conventional high-flow oxygen therapy.
7. In addition, the technique is considered easy and simple for the medical staff and nurses, and can be used in different areas (emergency, hospitalization, critical care unit, weaning centers) and even at home [4].
Currently available evidence has demonstrated that HFNC therapy is an alternative for the treatment of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, hypercapnic respiratory failure, acute heart failure, as rescue therapy preventive therapy in post-extubation respiratory failure and in specific conditions such as bronchoscopy [5].
We believe that high-flow nasal cannula treatment should not be confused with high flow oxygen therapy of venturi masks. According to detailed mechanisms of action, HFNC is not limited to being only an oxygen therapy system but also behaves as a true treatment that can be used in different clinical scenarios, generating physiological benefits that result in the reduction of respiratory work. In addition, in venturi type masks, the air is not humidified and complications such as dryness and nasal pain are common, generating a poor tolerance to oxygen therapy. The benefits of proper humidification and heating of the gas delivered with HFNC therapy allow better comfort and tolerance of the patient with easy adherence to the treatment. All this contributes to making HFNC be considered a technique of choice in patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure. The growth in its use associated with easy acceptance for patients and the expansion in its application show us that HFNC is a promising therapy.

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."